Varicocele is a condition that affects millions of men worldwide, often leading to fertility issues and chronic discomfort. Early detection is crucial for preventing complications and ensuring timely intervention. In this article, we will delve into the basics of varicocele, its early signs, diagnostic steps, and the importance of seeking medical attention.
I. What Is Varicocele?
1. Basic Definition and Anatomy
Varicocele is essentially the enlargement of the veins within the scrotum, similar to varicose veins in the legs. This condition is most commonly observed on the left side due to anatomical differences, such as the longer left testicular vein and its unique drainage system. Understanding the venous structures in the scrotum is key to recognizing varicocele.
Varicoceles are graded from mild to severe based on their size and impact on testicular function. Early detection and grading are vital for determining the appropriate course of action. The severity of a varicocele can be classified into three grades: Grade I can be felt by hand only during straining, Grade II can be felt by hand when relaxed, and Grade III can become clearly visible at a distance, even at complete rest.
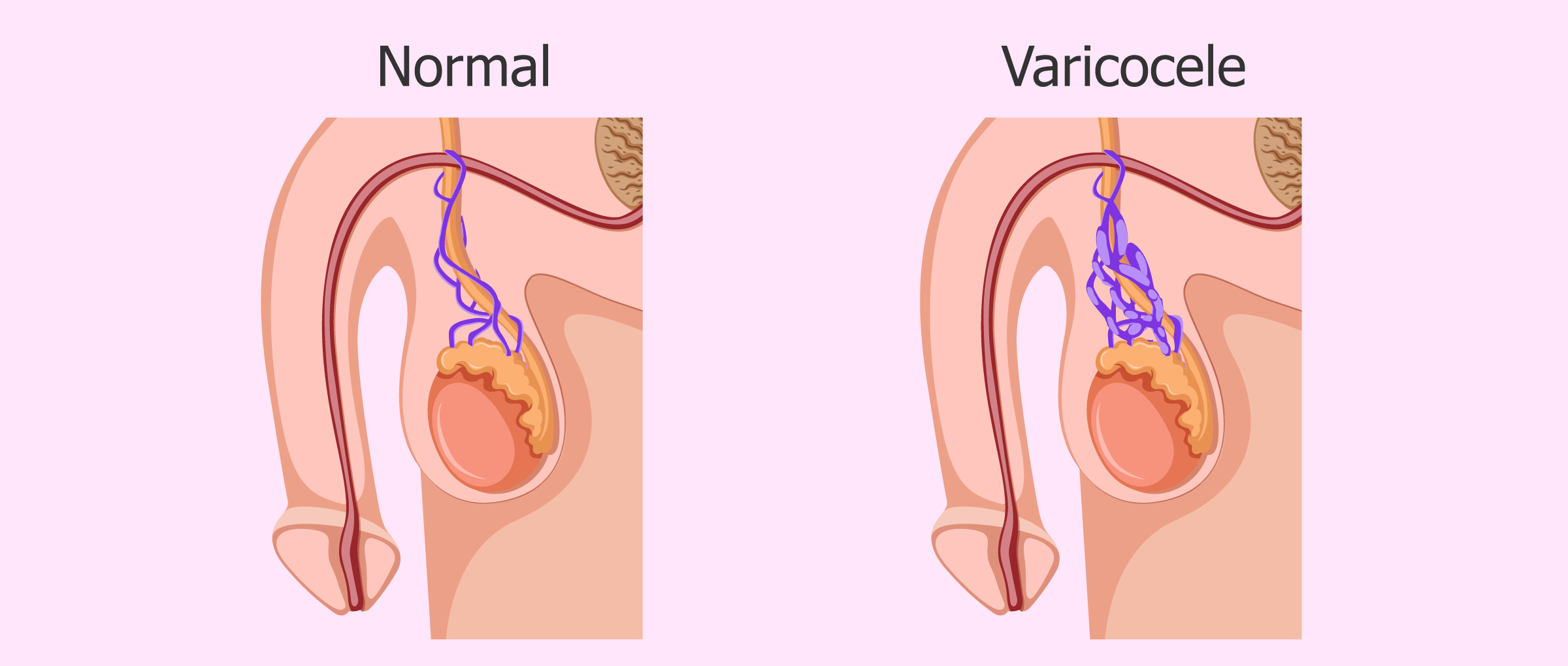
2. Why Early Detection Matters
Early detection of varicocele is crucial for several reasons:
- Preventing Fertility Issues and Complications: Varicocele is a common cause of male infertility, affecting sperm quality and testosterone production. Treating varicocele can significantly improve fertility outcomes.
- Reducing Chronic Pain and Testicular Damage: Untreated varicoceles can lead to chronic pain and testicular damage over time. Early intervention helps mitigate these risks.
- Improving Quality of Life: By addressing varicocele early, men can avoid long-term discomfort and improve their overall quality of life.
II. Common Early Signs
1. Physical Symptoms
Varicocele often presents with noticeable physical symptoms:
- Dull Ache, Swelling, or “Bag of Worms” Feeling: The enlarged veins can feel like a bag of worms and may cause a dull ache or swelling in the scrotum.
- Discomfort After Standing for Long Periods: Symptoms often worsen when standing or exerting oneself for extended periods and may improve when lying down.
- Visible Veins: In more severe cases, the enlarged veins may be visible through the skin.
2. Subtle Indicators
Some signs may be more subtle:
- Slight Testicular Asymmetry: One testicle may appear larger than the other due to the swelling.
- Occasional Scrotal Heaviness: A feeling of heaviness in the scrotum, especially after prolonged standing.
- Low Sperm Count: Men with varicocele may experience a low sperm count, which can be detected through semen analysis.
III. Diagnostic Steps
1. Self-Examination
Regular self-examinations are essential for detecting lumps or unusual vein enlargements. Here’s how to perform a self-testicular examination:
- Stand Up: Stand in front of a mirror and look for any visible swelling.
- Lie Down: Lie down and check if the swelling disappears.
- Check for Lumps: Gently feel your testicles for any lumps or unusual vein enlargements.
Regular checks can help identify varicoceles early. You might discover you have a varicocele during a regular testicular self-examination.
2. Professional Evaluation
A professional evaluation typically involves:
- Ultrasound Imaging and Physical Exam: These are used to confirm the presence and severity of varicocele. Ultrasound can show backward flow of blood in the swollen testicular veins.
- Medical History and Potential Risk Factors: Discussing medical history and potential risk factors helps in understanding the condition better.
- Semen Analysis: This may be recommended to assess sperm quality and count.
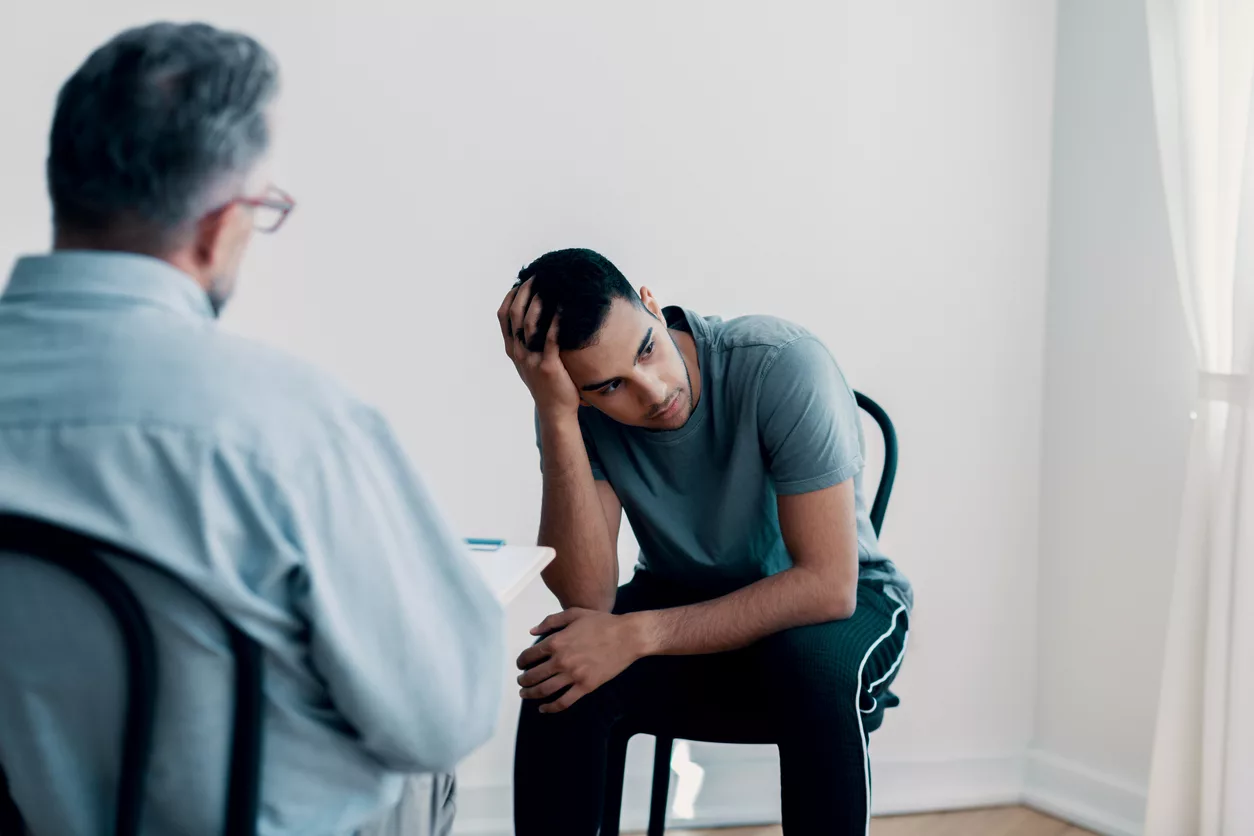

IV. The Importance of Timely Intervention
1. Possible Next Steps
After diagnosis, the next steps depend on the severity of the varicocele:
- Monitoring Mild Varicoceles vs. Opting for Treatment: Mild cases may be monitored, while more severe cases may require surgical intervention.
- Fertility Considerations if Planning for Children: If you are planning to have children, treating varicocele can improve fertility outcomes.
- Lifestyle Changes: In some cases, lifestyle adjustments such as avoiding prolonged standing or wearing supportive underwear may be recommended.
2. Preparing for a Doctor’s Visit
Before visiting a doctor, consider the following:
- Questions to Ask Regarding Tests and Treatments: Ask about the diagnostic tests, treatment options, and potential outcomes.
- Understanding Referral to Specialists (Urologists): If necessary, understand why a referral to a specialist might be recommended.
- Discussing Fertility Concerns: If fertility is a concern, discuss this with your healthcare provider to explore options.
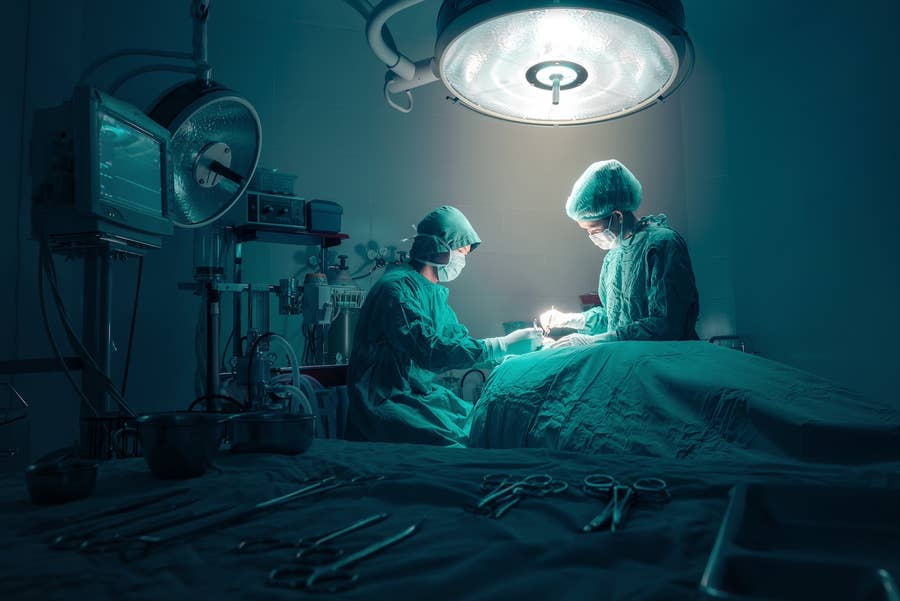

3. Surgical Treatment Options
Surgical treatment for varicocele is often recommended for severe cases or when fertility is a concern. The goal of surgery is to block the abnormal veins to prevent blood from pooling and reduce swelling. Common surgical techniques include:
- Open Surgery: This involves making a small incision in the abdomen or groin to access and repair the affected veins.
- Laparoscopic Surgery: A minimally invasive procedure using small incisions and a camera to visualize the area.
- Percutaneous Embolization: A non-surgical procedure where a catheter is inserted through a vein in the neck or groin to block the abnormal veins.
V. Men's Health Vietnam Center Services
At the Men's Health Vietnam center, our comprehensive services are designed to address varicocele and other male health issues effectively. Our team of specialists provides thorough evaluations, personalized treatment plans, and support for fertility concerns. By focusing on early detection and intervention, we help men maintain optimal health and address potential complications proactively.
- Address: 7B/31 Thanh Thai Street, Ward 14, District 10, Ho Chi Minh City, Vietnam
- Website: menhealth.vn
- Fanpage: facebook.com/trungtamsuckhoenamgioi
- Contact: (+84) 902 353 353
 0902 353 353
0902 353 353 Giờ làm việc: 08:00 - 20:00
Giờ làm việc: 08:00 - 20:00 7B/31 Thành Thái, Phường Diên Hồng, TP. HCM
7B/31 Thành Thái, Phường Diên Hồng, TP. HCM
