I. Understanding Prostate Inflammation (Prostatitis)
1. What is Prostatitis?
Prostatitis refers to inflammation of the prostate gland, a walnut-sized organ located below the bladder that produces seminal fluid, a key component of semen. This condition affects men of all ages, with approximately 50% experiencing it at some point in their lives. Prostatitis is classified into four types by the National Institutes of Health (NIH):
- Acute Bacterial Prostatitis: Caused by a sudden bacterial infection, leading to severe symptoms.
- Chronic Bacterial Prostatitis: A recurring bacterial infection causing prolonged inflammation.
- Chronic Prostatitis/Chronic Pelvic Pain Syndrome (CP/CPPS): The most common form, often without a clear cause, characterized by persistent pelvic pain.
- Asymptomatic Inflammatory Prostatitis: Inflammation without noticeable symptoms, often detected during unrelated medical evaluations.
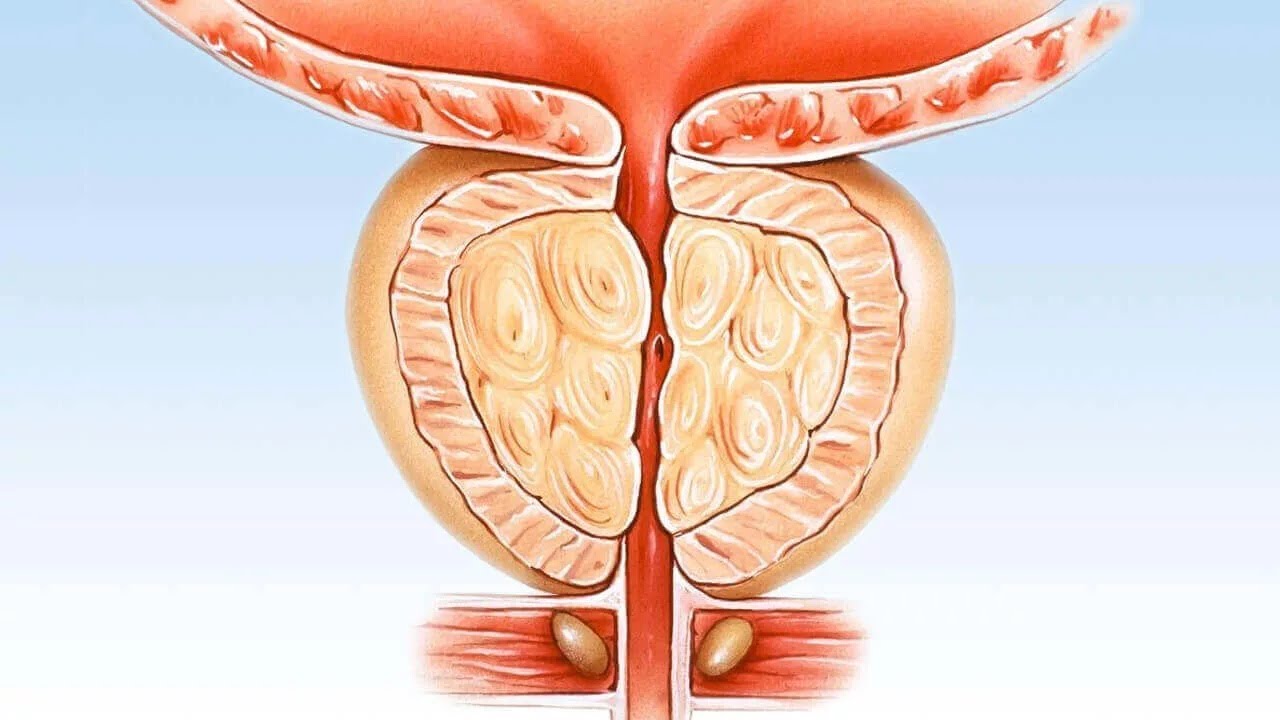
2. Causes of Prostate Inflammation
Prostatitis can stem from various triggers, including:
- Bacterial Infections: Pathogens like Escherichia coli or Chlamydia trachomatis can invade the prostate, causing acute or chronic infections.
- Autoimmune Responses: The immune system may mistakenly attack prostate cells, leading to inflammation.
- Nerve Damage or Physical Injury: Pelvic trauma or nerve issues can contribute to inflammation.
- Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs): Infections in the urinary tract can spread to the prostate.
- Unknown Factors: In CP/CPPS, the exact cause often remains unidentified, complicating treatment.
II. How Prostatitis Impacts Male Fertility
1. The Prostate’s Role in Fertility
The prostate gland plays a vital role in male reproduction by producing seminal fluid, which nourishes and protects sperm during ejaculation. It also aids in preventing semen backflow into the bladder, ensuring effective sperm delivery. Any disruption to these functions can impair fertility.
2. Direct Effects on Sperm Quality
Prostatitis can negatively affect sperm quality through several mechanisms:
- Increased White Blood Cells (Leukocytospermia): Inflammation often leads to elevated white blood cell counts in semen, which can damage sperm by producing reactive oxygen species (ROS). ROS cause oxidative stress, impairing sperm motility, morphology, and DNA integrity.
- Inflammatory Cytokines: Studies show that prostatitis patients have higher levels of pro-inflammatory cytokines (e.g., IL-1β, TNF-α, IL-6) in seminal plasma. These cytokines are associated with reduced sperm concentration, motility, and viability. A 2014 meta-analysis of 999 CP/CPPS patients confirmed significant declines in these parameters compared to healthy controls.
- Bacterial Infections: Pathogens like Chlamydia trachomatis or Ureaplasma urealyticum can directly harm sperm by triggering immune responses or causing epididymal obstructions, leading to conditions like obstructive azoospermia (no sperm in ejaculate).
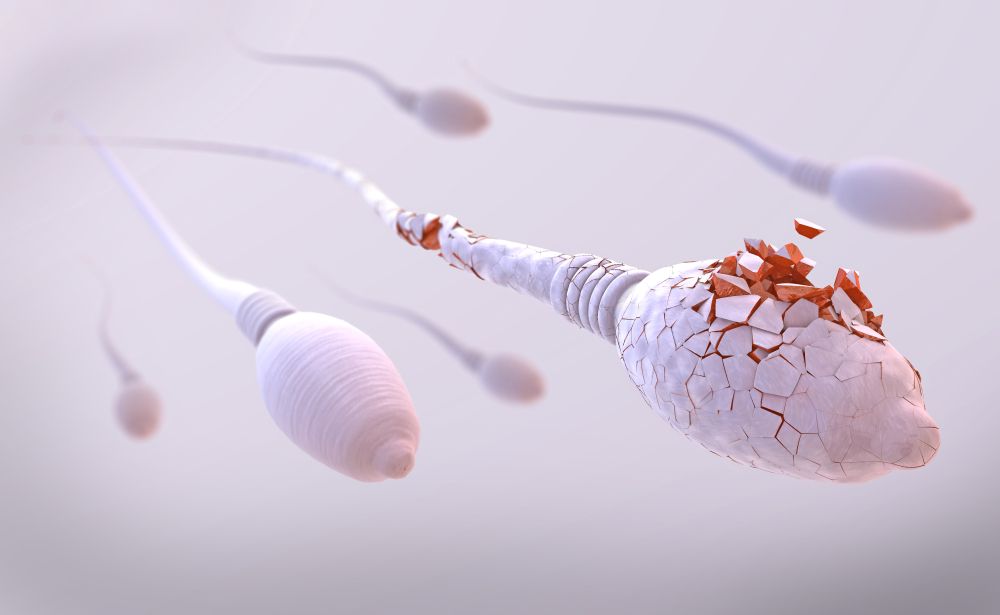
3. Indirect Effects on Fertility
Prostatitis can also indirectly impair fertility by affecting prostate function and sexual health:
- Ejaculation Problems: Painful ejaculation or hematospermia (blood in semen) can result from inflammation, discouraging sexual activity and reducing conception chances.
- Prostate Dysfunction: Inflammation may alter the quality of prostatic fluid, reducing its ability to support sperm function.
- Erectile Dysfunction and Decreased Libido: Chronic pain from prostatitis can lead to sexual dysfunction, further complicating fertility efforts.
- Obstruction of Semen Flow: In older men, an enlarged prostate (benign prostatic hyperplasia, or BPH) combined with inflammation can obstruct semen flow or cause retrograde ejaculation, where semen enters the bladder instead of exiting the penis.
4. Controversies in Research
While many studies link prostatitis to reduced fertility, some findings are inconsistent. For example, certain research indicates no significant differences in sperm motility or morphology between prostatitis patients and healthy individuals. These discrepancies highlight the need for further investigation to clarify the precise impact of prostatitis on fertility.
III. Treatment Options to Mitigate Fertility Issues
1. Addressing the Root Cause
Effective treatment of prostatitis can improve fertility outcomes by reducing inflammation and restoring prostate function:
- Antibiotics for Bacterial Prostatitis: Bacterial infections are treated with targeted antibiotics (e.g., fluoroquinolones) that penetrate the prostate effectively. Studies suggest that eliminating harmful inflammatory cells through antibiotic therapy can enhance sperm quality.
- Anti-Inflammatory Medications: Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) can reduce inflammation and alleviate symptoms in CP/CPPS cases.
- Lifestyle Modifications: An anti-inflammatory diet rich in omega-3 fatty acids, antioxidants, fruits, vegetables, and nuts can support prostate health. Reducing stress, quitting smoking, and limiting alcohol intake also contribute to better outcomes.
2. Advanced Fertility Interventions
For men with persistent fertility issues due to prostatitis, advanced reproductive technologies offer solutions:
- Epididymal Sperm Aspiration (PESA/MESA): These outpatient procedures retrieve sperm directly from the epididymis for use in assisted reproductive technologies (ART) like in vitro fertilization (IVF). They are effective for men with obstructive azoospermia caused by prostatitis-related blockages.
- Sperm Banking: Men anticipating treatments (e.g., for prostate cancer) that may further impair fertility can preserve sperm through cryopreservation. Frozen sperm remains viable for decades and can be used for ART.
- Management of Medication Side Effects: Some medications for prostatitis or BPH, such as alpha-blockers (e.g., tamsulosin), can reduce sperm count or ejaculation volume. Consulting a urologist to adjust medications can minimize these effects.
IV. Preventive Measures and Lifestyle Recommendations
Preventing prostatitis can safeguard fertility. Key strategies include:
- Regular Medical Checkups: Routine urological exams can detect early signs of prostate issues, allowing timely intervention.
- Healthy Diet: Consuming anti-inflammatory foods and avoiding processed foods or excess sugar supports prostate and reproductive health.
- Safe Sexual Practices: Reducing the risk of sexually transmitted infections (STIs) like Chlamydia can prevent prostatitis.
- Stress Management: Practices like meditation or exercise can reduce stress-related inflammation.
V. Men’s Health Services at Men’s Health Vietnam Center
The Men’s Health Vietnam Center offers comprehensive services to address prostate inflammation and its impact on fertility. Their team of experienced urologists and fertility specialists provides:
- Diagnostic Evaluations: Advanced diagnostics, including semen analysis, urine flow tests, and prostate examinations, to identify the cause of prostatitis and its effects on fertility.
- Personalized Treatment Plans: Tailored treatments, from antibiotics to minimally invasive procedures like the Urolift for BPH, to restore prostate health without compromising fertility.
- Fertility Preservation: Sperm banking and ART options for men facing prostatitis or related conditions.
- Holistic Care: Guidance on lifestyle changes and anti-inflammatory diets to support long-term prostate and reproductive health.
By consulting with experts at Men’s Health Vietnam Center, men can address prostatitis effectively, preserve their fertility, and navigate the path to parenthood with confidence. For more information or to schedule a consultation, visit their website or contact their offices directly.
- Address: 7B/31 Thanh Thai Street, Ward 14, District 10, Ho Chi Minh City, Vietnam
- Website: menhealth.vn
- Fanpage: facebook.com/trungtamsuckhoenamgioi
- Contact: (+84) 902 353 353
 0902 353 353
0902 353 353 Giờ làm việc: 08:00 - 20:00
Giờ làm việc: 08:00 - 20:00 7B/31 Thành Thái, Phường Diên Hồng, TP. HCM
7B/31 Thành Thái, Phường Diên Hồng, TP. HCM
